
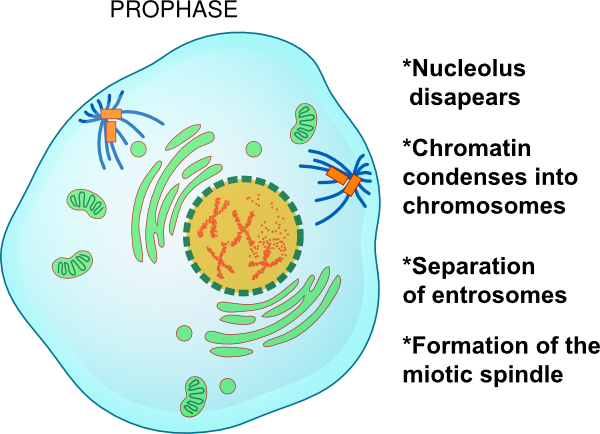
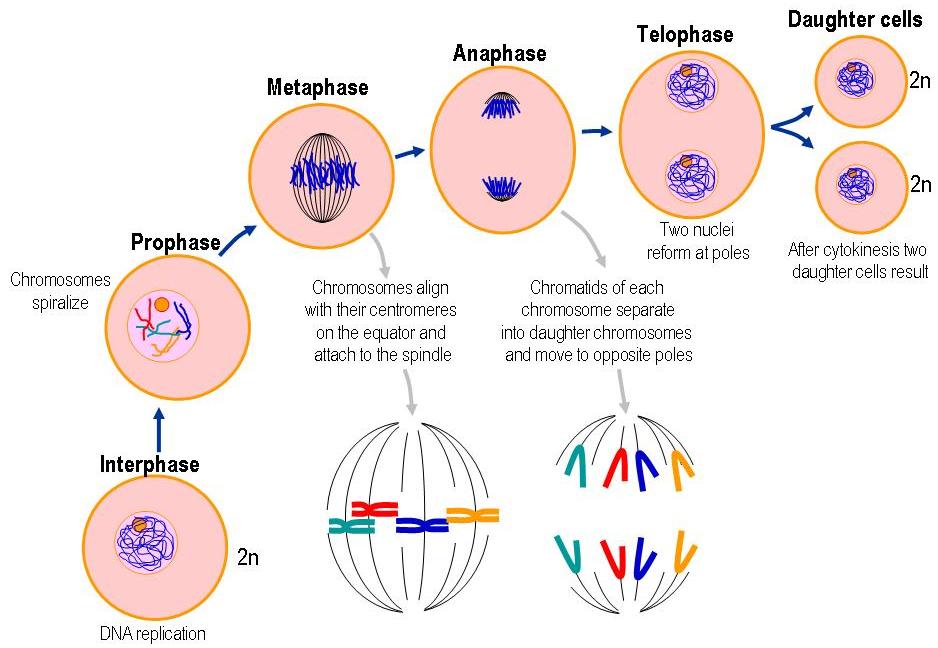
Where does mitosis occur? Mitosis happens in the somatic cells, particularly where the nucleus is at. Prior to entering the mitotic phase, the cell has a control mechanism called G2-M DNA damage checkpoint that ensures the cell is ready for mitosis. After replication, the newly synthesized DNA molecules are checked and repaired if damaged. If it enters the interphase, the cell would prepare itself for cell division by entering the S phase, where DNA replication occurs. In summary, the cell may enter either the resting phase or the interphase following cell division. The cell cycle consists of these fundamental events: (1) resting phase (Gap 0), (2) interphase (Gap 1, S phase, Gap 2), and (3) cell division (i.e. The somatic cells of the eukaryotic body go through a sequence of biological events called the cell cycle. Mitosis diagram Cell Cycle Overview Schematic diagram of the cell cycle. These mitosis facts and info are depicted in the illustration below. Other characteristics that define mitosis are as follows: genetic recombination does not happen during mitosis and the chromosome number is expected to be the same after mitosis it is not reduced to half. Thus, a single cell results in two cells right after mitosis whereas a cell results in four cells after meiosis. In mitosis, the cell divides once whereas in meiosis the cell divides two times. In contrast, the sex cells divide by meiosis wherein the outcome is the production of cells that are genetically different from the original cell. The somatic cells divide mitotically to produce daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Mitosis is a form of cellular division that involves the somatic cells whereas meiosis is a cell division employed by the sex cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
